
회원게시판
![]() > 회원마당 > 회원게시판
> 회원마당 > 회원게시판
- 작성자
- 관리자
- 작성일
- 2021-10-28
- 조회
- 498
연축성 발성장애와 후두 내 Botox injection
성균관의대 강북삼성병원 이상혁
연축성 발성장애란
연축성 발성장애(spasmodic dysphonia)는 후두에 국한적으로 발생하는 근긴장 이상으로 후두근육의 불수의적 연축(involuntary spasm)으로 인하여 발생하는 발성장애이다. 아직까지 원인이 정확히 밝혀져 있지 않으며 특발성인 경우가 가장 많다. 약 20%의 환자는 자동차 사고와 같은 외부손상이나 상기도 감염 후에 증세가 발생하며, 약 45-65%의 환자는 소아기에 볼거리나 풍진을 앓은 과거력이 있다. 최근에는 뇌의 중추 음성신경 조절기전 네트워크 장애로 발생하는 다양한 질환의 모음이라는 것이 밝혀졌다.
연축성 발성장애의 증상
연축성 발성장애는 30-50세 여성에서 주로 나타나며, 스트레스가 높은 기간이나 상기도 감염 후에 발생하는 경우가 많다. 병의 진행은 발생 첫해에는 점진적인 양상이며 이후에는 만성적인 상태가 된다. 연축성 발성장애의 특징적인 음성 단절(voice break)은 웃을 때나 노래할 때는 잘 나타나지 않지만 정신적인 긴장이 있을 때는 더욱 악화되는 경향이 있다. 연축성 발성장애는 내전형, 외전형, 그리고 복합형으로 분류하는데, 보통 내전형이 80-90%정도로 대부분을 차지하고 있다. 내전형 연축성 발성장애의 경우 갑상 피열근(thyroarytenoid muscle)과 외측 윤상 피열근(lateral cricoarytenoid muscle)의 불수의적이고 과도한 성대 수축에 의한 음성이 특징을 보인다. 외전형 연축성 발성장애는 성대를 열리게 하는 후 윤상 피열근 (posterior cricoarytenoid muscle)의 갑작스러운 연축에 의해 발생하는 성대개방 (glottic opening)에 의해 생기는 기식성 단절(breathy speech break)이 특징이다.
연축성 발성장애와 근긴장성 발성장애의 감별진단
증세가 심한 근 긴장성 발성장애(muscle tension dysphonia)는 음성이 연축성 발성장애와 비슷하여 감별하기 어려운 경우가 많다. 감별 점으로는 연축성 발성장애는 말 과제 특이성 (task specificity)과 비자발성을 보이며, 울기, 웃기, 속삭이기, 노래, 하품하기, 가성에서와 같이 비언어적 발성에서는 정상 소견을 보이지만, 근 긴장성 발성장애는 모든 발성에 영향을 받는다. 음성 단절의 경우 두 질환 모두에서 보일 수 있으나, 연축성 발성장애는 근 긴장성 발성장애와 비교하여 빈도와 기간이 더 심한 양상을 보인다. 임상적 감별점으로는 근긴장성 발성장애는 음성치료나 정신과 치료에 좋은 반응을 보이지만, 연축성 발성장애는 그 치료효과가 떨어지는 경향이 있다. 반대로 연축성 발성장애는 보툴리눔 독소 성대주입술에 증상의 호전을 보이나 근 긴장성 발성장애에서는 효과를 보이지 않는다.
연축성 발성장애의 치료
연축성 발성장애의 주된 치료법은 언어치료, 약물치료, 보툴리눔 독소치료, 수술 등의 방법이 있으나 보툴리눔 독소의 성대 주입을 통하여 반복적인 화학적 탈신경이 가장 안전하고 효과적인 방법으로 알려져 있다. 이는 보툴리눔 독소를 양측 갑상 피열근에 주입하는 것으로 근전도 유도 하에서 양측 갑상 피열근에 근전도 바늘이 들어간 것을 근전도상에서 확인하면서 보툴리눔 독소를 주입하거나 후두 내시경으로 주사침의 위치를 확인하여 주입하게 된다. 드물게 만날 수 있는 외전형 연축성 발성장애의 경우 성대의 외전을 주관하는 후 윤상 피열근에 보톡스를 주입하기도 한다. 최근에는 굴곡형 후두 내시경을 사용하여 성대를 직접 관찰하면서 성대 근육에 직접 보툴리눔 독소를 주입하는 것이 주로 사용되며, 그 효과는 근전도 하에서 보툴리눔 독소 주입하는 것과 대등한 효과를 보인다.
보툴리눔 독소의 일반적인 주입량은 과거에는 표준용량 2.5U 정도를 주로 많이 사용하였으나, 술 후 기식음 (breathy voice), 흡입과 같은 부작용이 수일에서 수주까지도 발생하게 되어 최근에는 보통 1-1.5U 정도의 용량을 많이 주입하고 있다. 보툴리눔 독소 주입 후 환자는 하루, 이틀간은 아무 증세가 없다가 주입된 용량에 따라서 수일에서 수주간의 기식성 음성과 흡인, 사래 걸림 소견을 보인 후 음성단절이 줄어들어 좋은 목소리 상태를 유지하다가 다시 악화되는 것을 약 3-6개월 주기로 반복하게 된다.
* 아래는 연축성 발성장애와 근긴장성 발성장애의 감별진단에 대해서 음성과 후두영상을 통해 소개하고자 한다.
* 음성 및 영상 자료는 크롬 또는 마이크로소프트 엣지 브라우저에서만 재생가능하니 참고부탁드립니다.
(인터넷 익스플로러에서는 재생 안됨)
Spasmodic Dysphonia (SD)
• Adductor SD
- - Spasmodic hyperadduction of TVFs
- - Intermittent voice breaks in the middle of vowels
- - Strained-strangled, effortful voice quality
• Abductor SD
- - Abduction of true vocal folds (devoicing gesture)
- - Prolonged voiceless consonants & difficulty with voice onset following voiceless sounds
- - May have breathy voice quality
How is SD and MTD differential diagnosed?
• Auditory-perceptual evaluation
• Laryngeal Examination
• Laryngeal endoscopy
• Videostroboscopy
• Acoustic assessment of vocal functions
• Voice therapy as Diagnostic tool
• Neurologic evaluation
• Electromyography
Laryngeal endoscopy
AdSD
- - Task dependency
- - Normal or intermittent voice break at sustained vowel
MTD
- - Sustained contraction and hyper adduction of larynx at connected speech and sustained vowel
Videostroboscopy
• Stroboscopy is rarely useful in the diagnosis of SD, as the diagnosis is established on the basis of voice evaluation an laryngeal examination
• In severe SD, the acoustic signal of the voice is so irregular that a fundamental frequency cannot be identified
• Moreover the normal sound of the of the voice during shouting and laughter is strong evidence
•Stroboscopic examination is more often of value in patients with MTD, because the diagnosis of MTD is more dependent on the exclusion of other causes
•In cases of presumed MTD that do not response voice therapy, the possibility of structural pathology of the vocal fold, such as scar, sulcus or an obscure cyst, must be considered, and stroboscopic examination is indicated
Acoustic assessment of vocal functions
• Acoustic analysis
| - Intraword phonatory breaks - Frequency shift - Aperiodic segments |
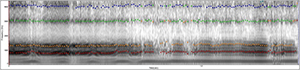 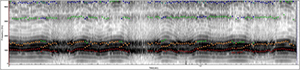 |
• Spectrogram
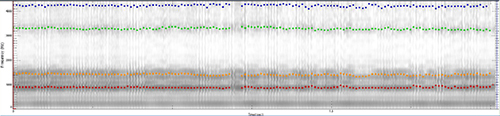
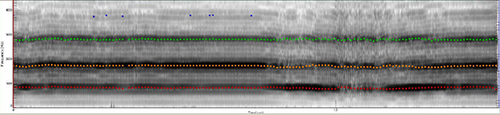
- - Abrupt voice breaks
- - Irregular wide-spaced vertical striations
- - Formant definition preservation
• Cepstral spectral index of dysphonia (CSID)
- - Task dependency
Voice therapy as diagnostic tool
• Typical trial voice therapy approaches
• If no improvements;
- Lidocaine nerve block test
How is SD and MTD Differential diagnosed?
Auditory-perceptual evaluation
| Spasmodic dysphonia | Muscle tension dysphonia | |
|---|---|---|
| /a/ | ||
| count | ||
| speech |
How is SD and MTD Differential diagnosed?
Laryngoscopy and stroboscopy
| • Spasmodic dysphonia | |
|---|---|
| • Muscle tension dysphonia | |
| • Spasmodic dysphonia(Sustained vowel + 가을 문장) | |
| • Spasmodic dysphonia(고음 발성 시 완화) | |
How is SD and MTD Differential diagnosed?
Acoustic evaluation
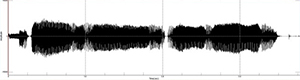
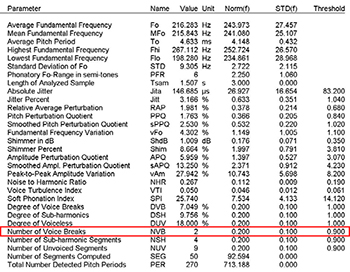
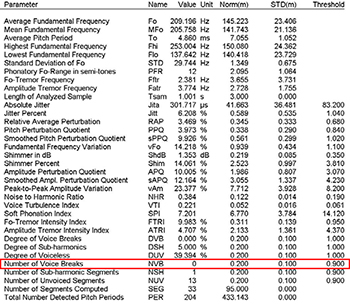
• Number of voice breaks of MDVP
| - Spasmodic dysphonia | |
|---|---|
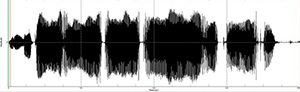  |
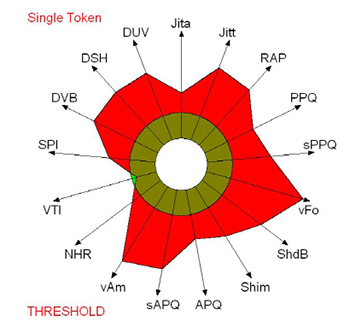 |
| - Muscle tension dysphonia | |
 |
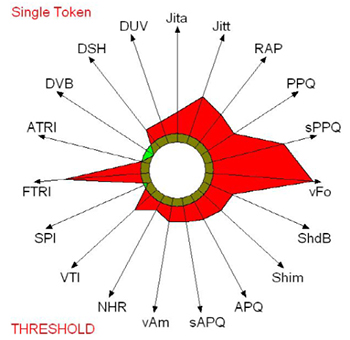 |
How is SD and MTD Differential diagnosed?
Acoustic evaluation
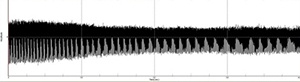
• Number of voice breaks of MDVP
| - Spasmodic dysphonia | |
|---|---|
  |
 |
 |
|
| - Muscle tension dysphonia | |
 |
 |
 |
|
How is SD and MTD Differential diagnosed?
Acoustic evaluation-spectrogram
• Spasmodic dysphonia
• Muscle tension dysphonia
How is SD and MTD Differential diagnosed?
Botox injection as diagnostic tool
• Spasmodic dysphonia - Adductor type
| /a/ | speech | |
| Pre-injection | ||
| 4d after BTX | ||
| 8wks after BTX |
• Muscle tension dysphonia
| /a/ | speech | |
| Pre-laryngeal massage | ||
| Post-laryngeal massage |
Summary
• SD is a neurologic disease, and MTD is a functional voice disorder
• The importance of a correct diagnosis of MTD and SD is critical at the treatment-selection moment
• MTD and SD are two voice disorders that present similar characteristics
| - differential diagnosis of AdSD and MTD can often be difficult. | ||
| AdSD | MTD | |
| Quality of voice | Strained voice quality with spastic voice break (breathy voice quality, voiceless consonant) |
Strangulated and strained voice quality |
| Task dependency | Task-specific | Not task-specific |
| Etiology | Neurologic | Compensatory or psychological |
| Tremor | Frequent | Rare |
| Treatment | Mostly treated by botulinum toxin injection Not respond to voice therapy | Mostly treated by voice therapy |
| Spectral findings | ||
| abrupt voice breaks | + | - |
| irregular vertical striationse | + | _ |
| high-freq. spectral noise | Some | Excessive |
• Differential diagnosis between SD and MTD is primarily based on clinical evaluation and standard laryngeal examination, and sometime acoustic analysis also give good information
• Clinicians should be aware of the specific vocal characteristics of each disease to promote advancement of our field through refinement of diagnostic skills and therapeutic outcome
• A multidisciplinary approach and cooperation between doctors (otolaryngologists, psychiatrists) and SLP is crucial to get a good clinical results






